Results available within 48 hours of test arrival to our partner labs
All tests are processed
in CLIA certified &
CAP accredited labs
Free shipping to your home and to
the laboratory
Male Executive Wellness At-Home Blood Test
Price
Our at-home Men Executive Wellness test is our most comprehensive test for men. It helps monitor multiple systems such as testosterone, prostate, heart, kidneys, liver, and more.
This test comes with 10 year heart attack probability and kidney damage analytics.
Online & PDF results are typically available 3-5 days after our lab receives your test.
Note: These tests are for informational purposes only. They are not meant to substitute medical advice, nor they’re supposed to diagnose any disease.
What Tests Are Included?
Results available within 48 hours of test arrival to our partner labs
All tests are processed
in CLIA certified &
CAP accredited labs
Free shipping to your home and to
the laboratory


Male Executive Wellness At-Home Blood Test
Price


Male Executive Wellness At-Home Blood Test
If you’re wondering how to test for heart disease risk, liver disease risk, libido issues or metabolism problems - the Male Executive Wellness test by Lab Me is a solid start. Maybe you are worried or want to take control of your health, no matter the case the Lab Me Male Executive Wellness is here to help.
Always share your results with your personal doctor - having tracked blood data can help your healthcare team make accurate decisions faster.
Who Should Consider Taking This At-Home Male Executive Wellness ?
If you’re wondering how to test for heart disease risk, liver disease risk, libido issues or metabolism problems - the Male Executive Wellness test by Lab Me is a solid start. Maybe you are worried or want to take control of your health, no matter the case the Lab Me Male Executive Wellness is here to help.
Always share your results with your personal doctor - having tracked blood data can help your healthcare team make accurate decisions faster.
Symptoms and Reasons to Test
The At Home Male Executive Wellness Test Is Encouraged If You Are:
- Constantly fatigued
- Irritable and have been having mood issues
- Experiencing erectile dysfunction, loss of libido or sexual drive.
- Under extreme stress
- Noticing enlargement of breast tissue
- Noticing decreasing fertility
- Having trouble gaining muscle
- Having trouble sleeping
- Have a strong family history of heart disease
- Taking cholesterol medication
- Have a family history of high cholesterol or heart disease
- Having trouble controlling weight
- Experiencing diarrhea, nausea or vomiting
- Smoking & drink alcohol frequently
- You aren't exercising
- A first-degree relative who has suffered a heart attack, cardiac stents, a stroke or has undergone bypass surgery
- Leading a sedentary lifestyle
- Suffering from diabetes, kidney disease, or an underactive thyroid gland.
- Experiencing severe fatigue
- Having low blood sugar
- Headaches
- Having brain fog or other cognitive difficulties
- Experiencing depression
- Prone to anxiety
- Having bone loss and weakness
- Having high-blood pressure
- Gaining or losing weight without reason
- It is recommended to take this test first thing in the morning, before 9am after fasting at least 6-8 hours.
Why Track?
Lab Me doesn’t use traditional dry blood spot cards like our competitors. We use a patented blood collection system that is FDA approved. It separates blood from plasma allowing us to have low variability and virtually identical results to arm drawn blood.
Regular testing of biomarkers can act as an early detection system. Especially if you’re not getting enough sleep, have improper nutrition, substandard training, unwise lifestyle choices or weak bone health. Lab Me helps by detecting non-optimal levels of blood biomarkers . For example high levels of cortisol which is an indicator of stress.
We use lab’s that are the same labs used by hospitals, major corporations, medical clinics and private doctors. They are CAP and CLIA certified and undergo regular audits and daily calibrations.
FIND OUT MORE ON WHY YOU SHOULD TRACKAdditional Info
Biomarkers explained
GGT is usually the first liver enzyme to rise in the blood when any of the bile ducts that carry bile from the liver to the intestines become obstructed, for example, by tumors or stones.
This makes it the most sensitive liver enzyme test for detecting bile duct problems.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
This is often called “bad cholesterol”. This is oversimplified as LDL cholesterol is essential for your health. But if you have too much LDL cholesterol it can build up on the walls of your arteries. This is called cholesterol plaque and it narrows your arteries and increases your risk of blood clots — putting you at risk of heart disease.
HDL stands for high-density lipoproteins. It is sometimes called the "good" cholesterol because it carries cholesterol from other parts of your body back to your liver. Your liver then removes the cholesterol from your body. LDL stands for low-density lipoproteins.
VLDL is a lipoprotein which is considered a “bad” form of cholesterol. Raised levels are a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Lipids
There are special transporters in your body called lipoproteins. They are like little cars that help drive around cholesterol to different parts of your body. Some of these drivers can be helpful and others not.
Monitoring and maintaining healthy levels of these lipids is important in staying healthy. While the body produces the cholesterol needed to function properly, the source for some cholesterol is the diet. Eating too much of foods that are high in saturated fats and trans unsaturated fats (trans fats) or having an inherited predisposition can result in a high level of cholesterol in the blood. The extra cholesterol may be deposited in plaques on the walls of blood vessels. Plaques can narrow or eventually block the opening of blood vessels, leading to hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis) and increasing the risk of numerous health problems, including heart disease and stroke.
LDL:HDL %
A high serum LDL:HDL ratio can be predictive of sudden cardiac death in middle-aged men. It is a good idea to keep this as a baseline over time to give a clearer picture of how your lifestyle is affecting your health.
Total Cholesterol is a measure of the total amount of cholesterol in your blood. It includes both low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
It’s important to remember that elevated cholesterol doesn’t mean a heart attack. In fact, only half of the people suffering from heart attacks have elevated cholesterol. It is simply part of the bigger picture.
Cholesterol is important for the body to manufacture hormones, vitamin D, bile acids, and help maintain the structure of your cells.
Total Cholesterol:HDL %
We determine your cholesterol ratio by dividing your total cholesterol by your HDL number. For instance, if your total cholesterol is 180 and your HDL is 82, your cholesterol ratio is 2.2. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), you should aim to keep your ratio below 5, with the ideal cholesterol ratio being 3.5.
Results for men
According to the Framingham Heart Study, a cholesterol ratio of 5 indicates average risk of heart disease for men. Men have double the risk for heart disease if their ratio reaches 9.6, and they have roughly half the average risk for heart disease with a cholesterol ratio of 3.4.
Results for women
Because women often have higher levels of good cholesterol, their cholesterol ratio risk categories differ. According to the same study, a 4.4 ratio indicates average risk for heart disease in women. Heart disease risk for women doubles if their ratio is 7, while a ratio of 3.3 signifies roughly half the average risk.
It’s important to remember that elevated cholesterol doesn’t mean a heart attack. In fact, only half of the people suffering from heart attacks have elevated cholesterol. It is simply part of the bigger picture
Cholesterol is important for the body to manufacture hormones, vitamin D, bile acids, and help maintain the structure of your cells.
Testosterone
You may need this test to find out whether a low sex drive is caused by a low level of testosterone. In recent years, healthcare providers have used testosterone therapy to treat both men and women with low sex drives.
Men with low levels of testosterone (hypogonadism) may have:
- Loss of sex drive
- Low energy
- Bone loss
- Infertility
The test is also done for men with andropause, or late-onset hypogonadism. This is a condition caused by decreased testosterone. Men with this condition may have:
- Anemia
- Depression
- Decreased bone density
- Lack of energy or fatigue
- Loss of muscle mass
- Poor concentration
- Erectile dysfunction or inability to have an orgasm
- Infertility
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA)
The PSA test can detect high levels of PSA that may indicate the presence of prostate cancer. However, many other conditions, such as an enlarged or inflamed prostate, can also increase PSA levels. Therefore, determining what a high PSA score means can be complicated.
Therefore tracking it overtime helps assist your baseline and assists in detecting deviations from your personal normal.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps keep your bones healthy and strong! It forms in the body when the sun is absorbed by your skin. Don’t fret – vitamin D deficiency is very common and can be fixed, but low levels can cause things like fatigue and sleep issues.
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone that is released by the adrenal gland in response to stress or low blood glucose. It is responsible for controlling the body’s blood sugar levels, regulating metabolism, acting as an anti-inflammatory, influencing memory formation, controlling salt and water balance, influencing blood pressure and helping the development of a fetus in pregnant women.
Glucose
Blood glucose measures the glucose levels in your blood. Glucose is a type of sugar. It is your brain & body’s main source of energy. A hormone called insulin helps move glucose from your bloodstream into your cells. Too much or too little glucose in the blood can be a sign of a serious medical condition. High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) may be a sign of diabetes, a disorder that can cause heart disease, blindness, kidney failure and other complications. Low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) can also lead to major health problems, including brain damage, if not treated.
hs-CRP
hs-CRP is a measure of C-reactive protein (CRP), a protein that the liver makes when there is inflammation in the body. While inflammation in the body can be beneficial in the right amounts, in order to help protect organs from injuries or infections, excessive inflammation has been linked to heart disease, stroke and more.
HBA1C
HbA1c is a measurement of the amount of glucose bound to the heme found in red blood cells. An HbA1c measurement lets you know how well your sugar levels have been controlled over the past 90 days—so if you want to take a closer look at your average blood glucose levels to better understand your body’s glycemic control, our HbA1c Test is a great place to start.
The % of Hemoglobin A1c refers to the amount of glycated hemoglobin in the blood. Glycated hemoglobin is red blood cells that have glucose attached to them. An A1c between 5.7-6.4% signals prediabetes. Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed when A1c is over 6.5%
Creatinine
Creatinine is a byproduct of muscle metabolism and gets excreted in the urine by the kidneys. This process is typically tightly regulated, making extremely low or high creatinine rare. Urinary creatinine is used as a control to make sure that other markers being tested are not reported inaccurately from kidney filtration problems. Your sample is collected four times throughout the day, and your results will reflect your levels during those times.
With this test we provide predictive insight into the amount of damage that has been done to your kidneys.
Shipping & Return Policy
Shipping
We ship most orders within 24-48 hours of receiving them. Depending on the shipping method you select at checkout you may receive your order within 2 to up to 5 days and it'll include a pre-paid label for you to ship the product to the lab.
Shipping Recommendations
It's important that you ship your sample the same day you take it. Please do not take your sample on Friday as that will cause delays in shipping. Ship your sample Monday thru Thursday on the same day you took it.
Return Policy
Due to the nature of our products, full refunds are not accepted for any open products. You can ship your un-used, un-open test kit back to us in it's original packaging within 7 days of delivery for store credit or a replacement kit. If you'd like a cash refund back to the original payment method, there will be a 25% re-stocking fee deducted from the refund amount.
Avoiding Errors In Your Results
TNP or Test Not Performed
What does it mean?
Less than 8% of our tests results in a TNP or Test Not Performed. This means that the machines could not analyze your sample for any of the following reasons below.
Hemolysis
This can occur due to factors like applying excessive pressure on the finger during blood collection or not properly drying the finger before using the lancet.
Not Enough Blood
In some cases, an inadequate amount of blood collected can result in inconclusive findings. Please apply at least 4 full-bodied blood drops as shown in the image of the instruction manual
Sample Contamination
Washing your hands with soap and not washing it all of correctly or applying too much alcohol on your finger before taking your sample, or taking a sample on a finger that was not been disinfected can lead to contamination of your sample
How to minimize your changes of an Error or TNP
To minimize the chances of receiving an inconclusive result, please follow these guidelines: Adhere closely to the provided instructions. Be gentle when collecting blood samples and ensure your finger is clean and dry before using the lancet. Promptly ship your sample to avoid heat exposure.
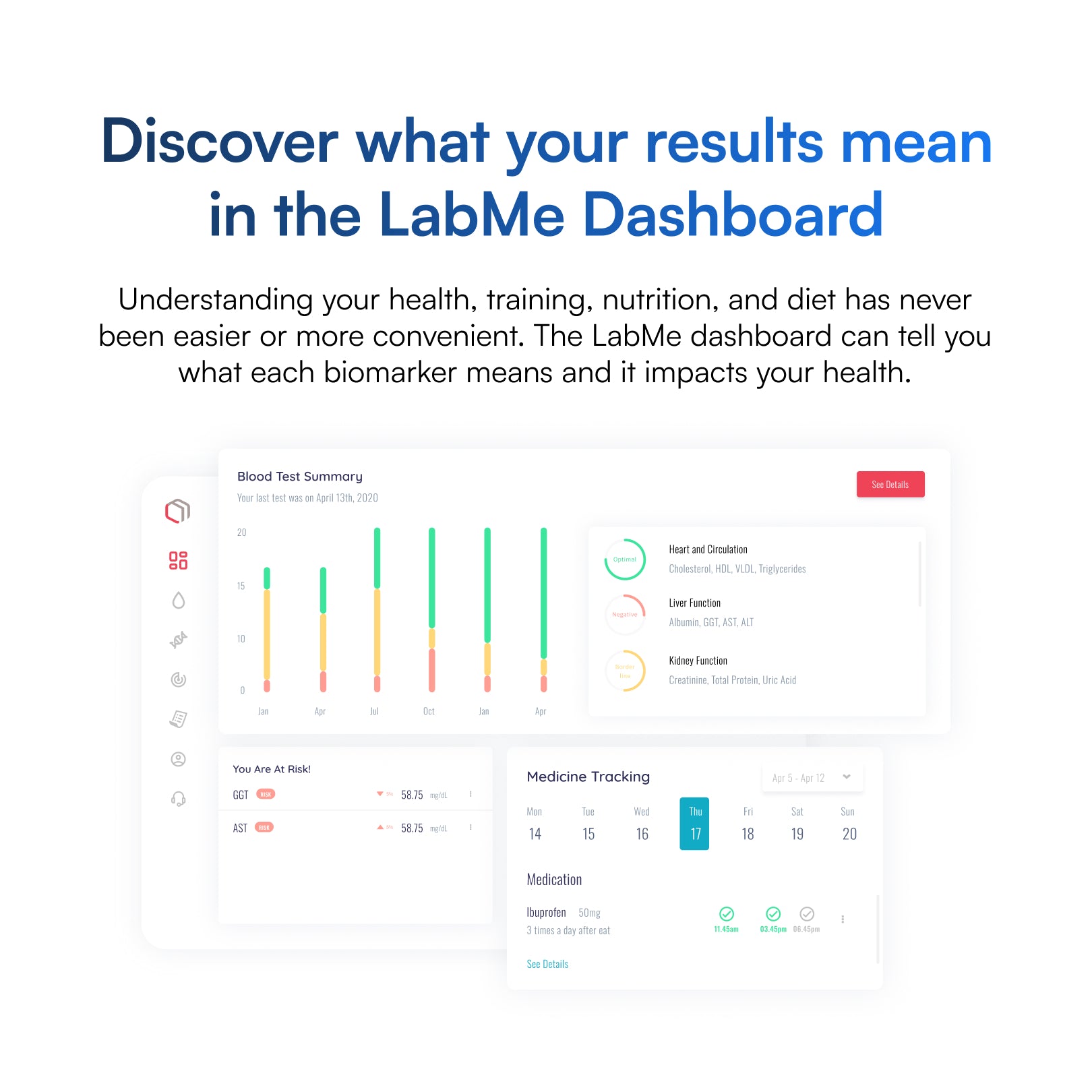
Discover what your results mean in the Lab Me Dashboard
Understanding your health, training, nutrition, and diet has never been easier or more convenient. The Lab Me dashboard can tell you what each biomarker means and it impacts your health.
The Lab Me Difference
Lab Me follows a rigorous validation process to assure each biomarker is capable of meeting all precision and reproducibility before inclusion on our test menu.
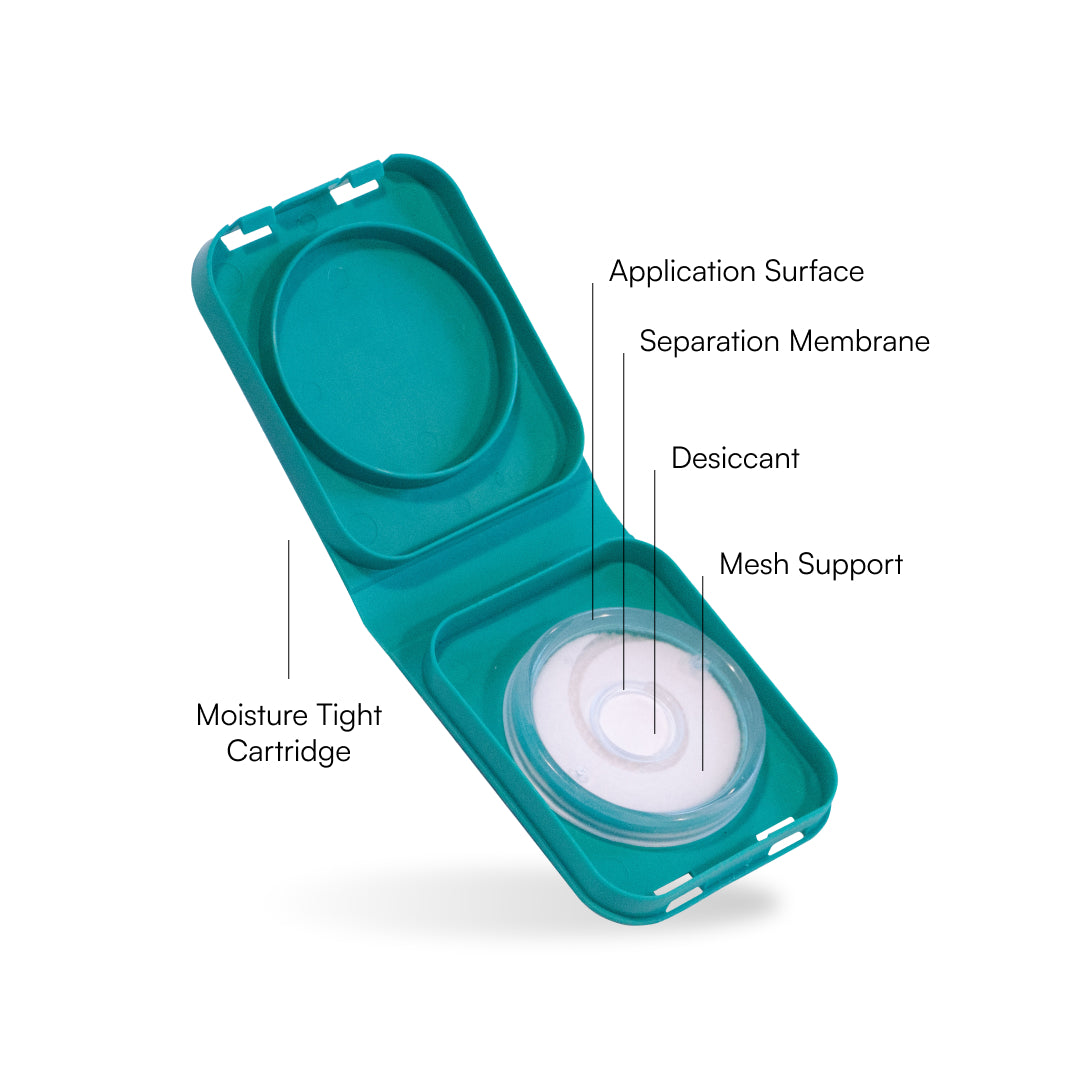
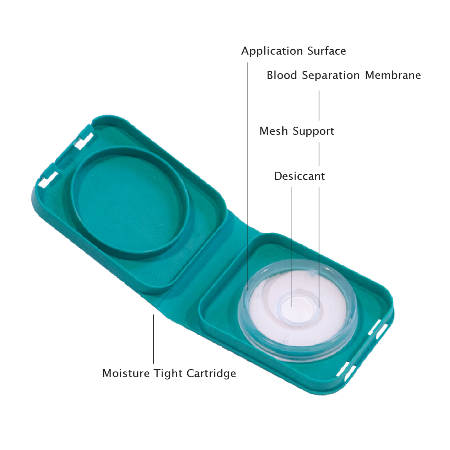
We use apatented plasma membrane separation system that outperforms traditional dry blood spot cards.
This collection device is a convenient way to collect a blood sample in the comfort and privacy of your home for laboratory analysis.
This is the only fast, easy, and needle-free collection device that requires 4 drops of blood from the fingertip.

FAST, SIMPLE & ACCURATE
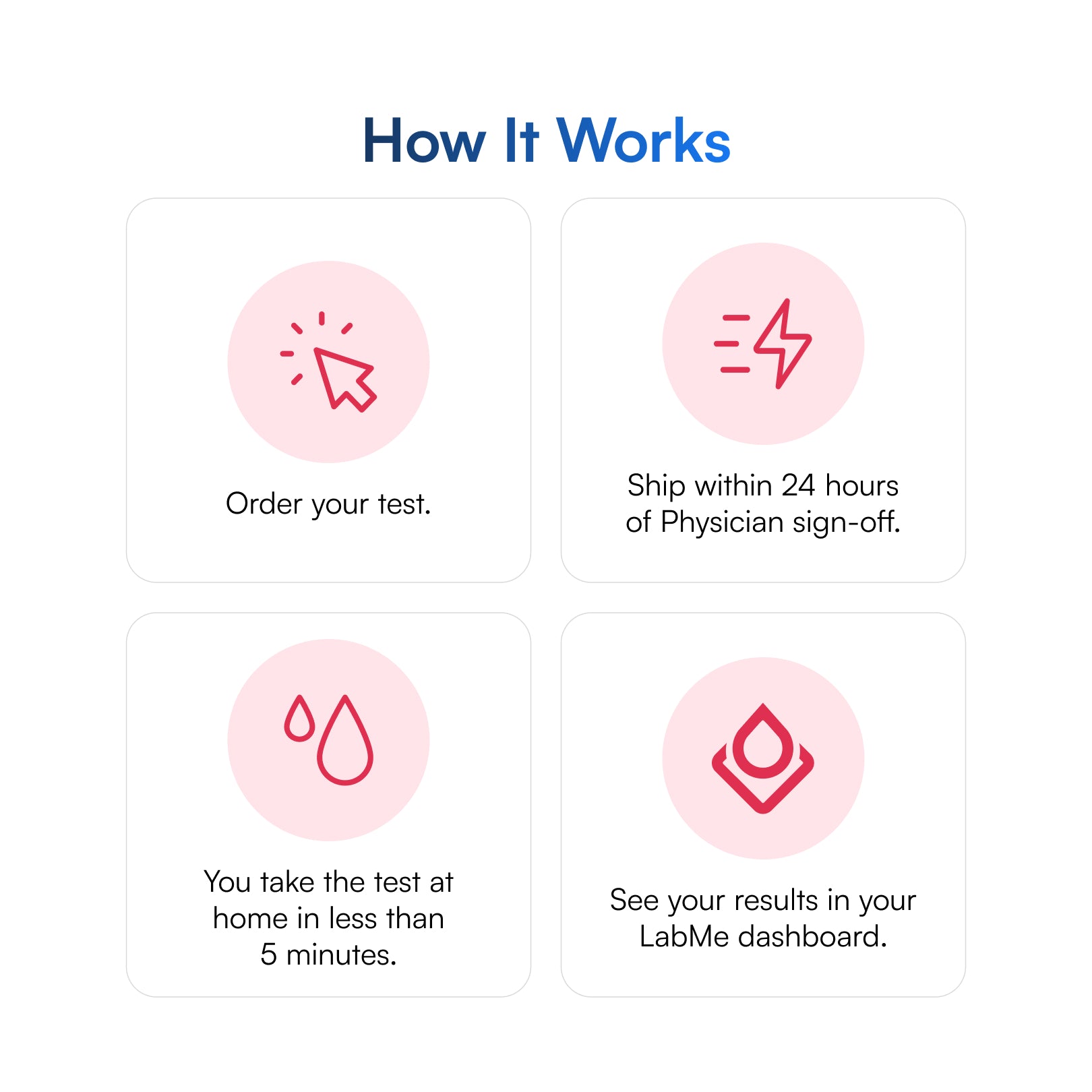
How To Get Started Today
Step 1Order your Lab Me test
Choose a test that fits your specific needs. We automatically get an MD to sign off so you avoid sitting in a doctor's office or clinic.
Step 2Take the test at home
Collect your specimen in the morning (8am is best). Return your sample within 3 days, using the prepaid shipping label provided.
Step 3Get your results within 48 hours
Once your sample arrives in the laboratory, confidential results will be available from your secure online account within 48 hours.
Hear From Other People That Care About Their Health